Introduction
All entrapment syndromes need exact clinical evaluation and require additional neuro-physiological examinations for a precise diagnosis. The most frequent symptoms are described below. Operative therapy in cases with persistent symptoms or neurological deficiencies consists of microsurgical decompression. The hospital stay is usually only one night and some operations can be done on an outpatient basis.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The median nerve in the distal underarm and inner side of the hand is entrapped.
This causes especially during the night pain in the thumb and the index fingers. There is a painful sensation of pins and needles and sometime a loss of strength also. Many patients complain of symptoms when they bicycle due to the position of he hands.
First therapeutic steps are anti-inflammatory medication and volar splints for the night.
When neuro-physiological examination shows a severe impingement an operation to achieve decompression will be indicated. By means of microsurgical technique the operation trauma is minimised so that no temporary fixation of the hand will be necessary.
Sulcus ulnaris syndrome
This entrapment syndrome is located on the inner elbow where the nerve is lying within a small groove before it disappears under the muscles of the forearm.
Typical complaints are local pain and pins and needles in the inner forearm and in the small fingers. Even weakness of the hand can appear. The microsurgical technique I employ avoids a conventional operation with new embedding and needs no fixation post-operatively. The hospital stay is normally only one night.
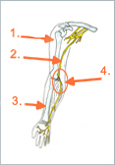
Schematic drawing:
1.) Upper arm bone
2.) Ulnaris nerve
3.) Radius bone
4.) Sulcus of nerve
Loge de Guyon syndrome
This entrapment syndrome is not frequent and is situated in the distal part of the ulnaris nerve where the nerve enters the hand.
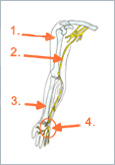
Schematic drawing:
1.) Upper arm bone
2.) Ulnaris nerve
3.) Radius bone
4.) Loge de Guyon
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
The entrapment is situated at the inner ankle of the foot. Pain is typically in the forefoot and the inner side of the foot especially when moving around a lot.


